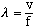
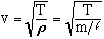
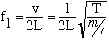
Answers
| Download PDF Document(242k) |
Printable (300dpi) GIF images:
Page 1(107k), Page 2(122k) Screen (100dpi) GIF images: Page 1(21k), Page 2(25k) |
Blank Homeworks
|
Download PDF Document(18k)
Download Word Document(147k) -- right click (Control + click on Mac) -- save file -- open file in MS Word |
Printable (300dpi) GIF images:
Page 1(84k), Page 2(78k) Screen (100dpi) GIF images: Page 1(15k), Page 2(14k) |
NAME: _______________________, Sect. #_______
| Physics 109 Homework # 3 | due Monday, October 1, 2001 |
formulae:
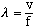
| 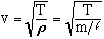
| 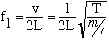
|
speed of sound in air: 340 m/s.
| 1. Find the phase shift between the two oscillations shown in the graph: phases shift = ___________ | 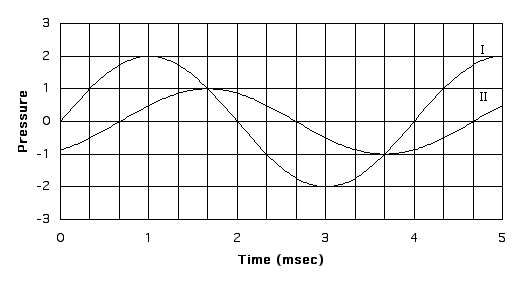
|
2. Wave length:
a)The range of hearing extends from about 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.f = ________________Hz.
3. Speed of propagation on String:
at the Steinway factory, a worker finds that 500 m of piano wire on a spool weigh 2 kg.4. The 60 cm long string of a viola is tuned to 200 Hz.
length = __________________
what length would produce 300 Hz?length = __________________
5. Consider two loudspeakers oscillating in phase playing the same tune. Your ear is 6.0 m from one speaker and 5.4 m from the other.
Which frequencies will you hear very little (cancel)?